When building a business online, providing the best user experience possible is one of the fundamental things to focus on. Collecting data about overall user behavior is always an alternative. Today, almost every website has access to those metrics.
To step up your game in fierce competition, you need to use something more specific. This is where website heatmaps come into the picture. The kind of data this insight tool gives you access to is essential for every company that wants to gain an edge in the market.
“A website heatmap tool helped me understand where I was going wrong with the placement of strategic buttons on my game. As soon as I spotted that something was not right in the heatmap, I ran a survey that confirmed my assumptions. Later on, by making one of the buttons more visible and easier to find, we’ve managed to reduce users’ bounce rate from 26% to 22%.” says Neal Taparia, Co-Founder of Spider Solitaire Challenge.
The concept of heatmaps is not new by all means. Many successful companies have years of experience using these web analytics tools. Using heatmaps may seem confusing, but using these tips and knowledge will make it easier than you think. Are you interested? Let’s dive in!
Scale insightful marketing content across the web.
We help you grow through expertise, strategy, and the best content on the web.
How to use website heatmaps

There are countless companies out there that are using them the wrong way. Heatmaps won’t be of any use for you if you can’t see beyond all those red, yellow, blue, and green shades on your web page.
Even the developers of these tools find it difficult to come up with terms and definitions that give you a clue about the complete picture. Often they oversimplify with vague terms that cause users to miss the point.
Not to mention that these terms differ depending on which heatmap application you use. In this regard, there is no consistency in either of the different heatmaps that are available.
In this guide, we are going to thoroughly explain everything you need to know about the proper use of heatmaps. This way, you will be finally able to get some actual value out of these complex tools. You will also be able to choose the right heatmap tool for your website and blog.
Gain insight by understanding visualized data
Visualized data is not only important that human brains process visuals 60,000 times faster than they do text but business intelligence with data visualization capabilities will offer an ROI of $13.01 back on every dollar spent. Heatmaps will only give you valuable information if you understand what kind of data is visualized by them. They are the raw material you need to work with to get the data you need. The first thing to understand about heatmaps is that they present color-coded numbers.
By embedding forms strategically across your website, you gain the ability to gather targeted data points, such as user demographics, preferences, and specific interactions. Form builders offer insights beyond mere click tracking; they capture user input, preferences, and intent, enabling businesses to gauge user sentiment, needs, and pain points.
You can see them on the TV during the weather forecast when the presenter shows the differences in temperature for the upcoming days. Applications of heatmaps include visualizing human voice, traffic congestion, energy efficiency in a house, and a wide range of other fields.
Since website owners started using them, it turned out that plenty of valuable information can be harvested with this method. Heatmaps allow you to map out the clicks, scrolling patterns, eye fixations, and mouse movements of your visitors. This is especially useful for improving custom web development projects, where user interaction data can guide tailored design decisions that enhance usability, boost engagement, and drive conversions.
This way, you can monitor and quantize user behavior. Whether you collect user-specific data or monitor the overall activity on your website, you can gather an incredible amount of useful information. The point is to be aware of the specific information each heatmap can give you and which information you are interested in.
To effectively analyze and utilize this data, consider pursuing online training on Tableau, which offers valuable skills for visualizing and interpreting complex data.
Heatmaps can answer your most pressing questions
Which elements are your visitors looking at when they arrive at your landing page? Where do they hover their mouse in the meantime? Which are the buttons they are most likely to click? These three questions can be answered by three different heatmaps.
For example, you might notice that users look at the product image and headline while completely missing the call to action. By looking at their mouse movement, you can quickly find out which content is the most interesting for them on a particular page.
Based on your findings, you can piece together the entire journey that users took on your website. This can give you plenty of room for improvement if you know how to use heatmaps the right way.
For instance, after identifying which elements are ignored or overlooked, A/B testing can help you experiment with different layouts or calls to action to see what performs best. Heatmaps, combined with A/B testing, offer a powerful way to optimize user experience.
Heatmaps can’t be classified by relevance, as their use depends on the information you are interested in.
Below, we are going to explain how to use each type of heatmap so that you can get the most value out of them.
How to use mouse tracking heatmaps
These are by far the most widely used heatmaps among online businesses. To collect data about mouse interactions, you need to insert a tracking code on your website. After giving it some time to collect data, you are going to see how viewers on your site use their mouse.
The code keeps track of all the mouse movement, clicking, and scrolling that happens on a web page. Next up, we are going to talk about these 3 types of mouse tracking heat maps.
Hover maps
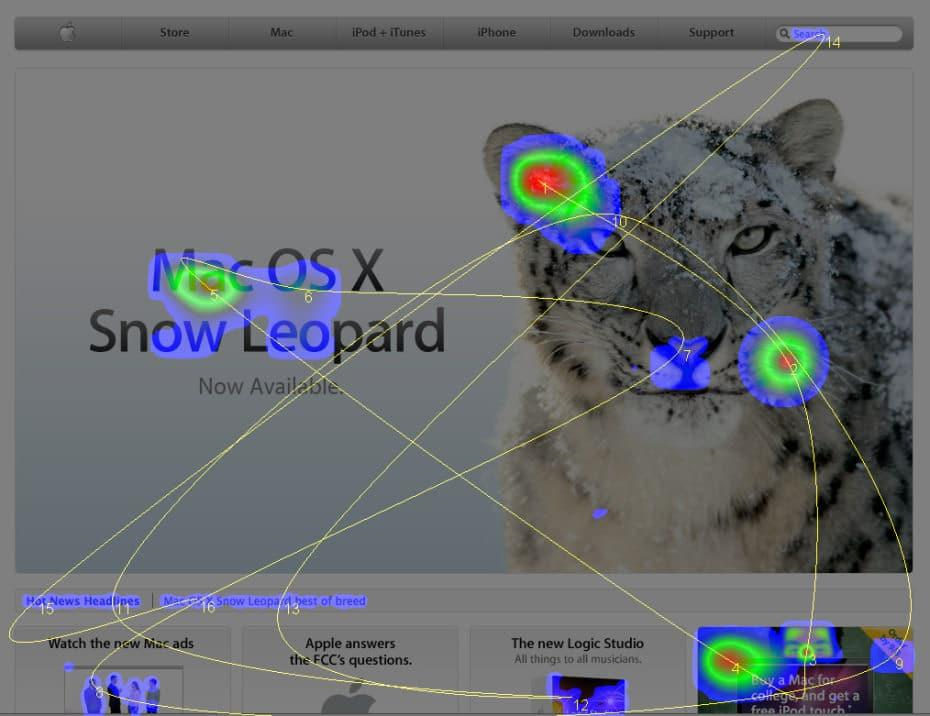
The reason we call these hover maps is that they track where users drag and hover their cursors after opening your web page. The red areas on these heatmaps show where their mouse spends the most time.
It comes naturally to visitors to drag their mouse to parts of the web page they are most interested in. Many of them are going to hover their mouse over the content that truly grabs their attention. However, others simply find a neutral spot for their cursor and leave it there while they read.
This is where the importance of using various types of heatmaps comes in. Because of these so-called “parkers”, you won’t be able to see the full story. It is important to mention that many heatmap vendors consider hover maps as a substitute for eye tracking, which is not true.
A study made by Google back in 2013 with the contribution of Carnegie Mellon University has proven that there is a weak link between the two. Google even quantified this comparison in 2007, which undoubtedly proves their point.
They approximated that predicting eye movements based on mouse movement can result in only 64% accuracy.
Click heatmaps

Often referred to as heatmaps based on clicks, these heatmaps can show you the most clicked parts of your web page. It might turn out that some photos, texts, or links attract clicks pretty well while others are left ignored. As you examine these heatmaps, you can even find links, buttons, or areas that don’t lead anywhere yet people click them.
For example, it often turns out that visitors try to click the image of your product. Many websites forget to add a link to them that takes the potential customer to the description page. This one and similar issues can be found out using click maps.
Then, all you need to do is to use the information you get and apply some hotfixes to your site. It is all about eliminating confusion about how your website works. People leaving forms halfway through filling them out is not unusual either.
With heatmaps, you can see exactly at which point they decide to bounce, allowing you to make improvements accordingly.
Scroll heatmaps
Scroll maps give you a nice color scale from the top of your web page to the bottom. They allow you to see how far each visitor gets on a particular web page by scrolling. Users usually stop scrolling when they find a content section they are interested in.
If you have a lot to show on your website yet your visitors don’t even scroll down, then there might be a problem. On a scroll heatmap, you can see whether users chose to learn more about your products or skipped the main content altogether.
You might have put immense effort into producing great content, yet your visitors don’t even get that far by scrolling. If this is the case, you can quickly find it out using scroll heatmaps and start working on those pages.
Mouse tracking heatmaps pros and cons
Pros:
- You only need to set them up on your website and they passively collect data from then on. All it requires is a tracking code and you can analyze the behavior of every one of your visitors.
- They provide you with a clear picture of how users behave on your website, pointing out various flaws. By mapping out their entire journey, you can adjust your site to their behavior.
- The ability to watch how individual visitors interact with your web page.
- There is a wide range of filters available for mouse tracking heatmaps that allow you to better understand the data.
Cons:
- Only works on live websites that are getting visitors. You can only improve your web pages after making them available to your audience. It not only takes time to collect the data but also to verify whether the applied changes have had the desired effect.
- Inserting an enormous factor for conversion rate. Also, these codes essentially collect user data, which is a delicate subject for large companies. As a result, the onboarding process takes longer than necessary.
Eye tracking heatmaps
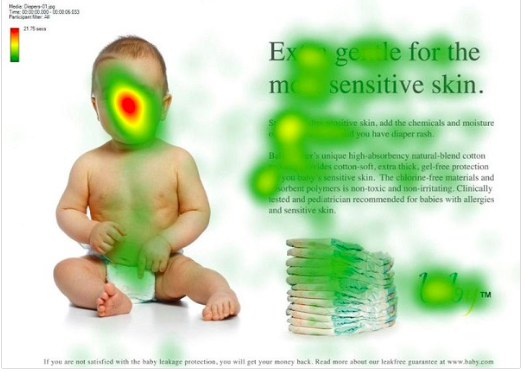
Heatmaps that track eye movement allow you to see your website through the eyes of someone who has never seen it before. Recording physical eye movements and assigning values to them as heatmaps is a next-level tactic that many companies use.
All you need to do is find some willing to interact with your website while wearing tracking devices. This way, you can perform a thorough study and end up with valuable data. Processing the data will allow you to discover flaws that would have otherwise remained hidden.
Another alternative to this method is a webcam-based approach that many vendors offer in the market. By giving participants some time to skim back and forth on a web page, you can end up with an interesting heatmap.
Just by looking at it, it will be obvious which are those sections that grab their attention. To get the most value out of eye-tracking heatmaps, it is best to try different time frames. For example, there is a big difference between knowing what your visitors are looking at in the first 2 seconds and in a 2-minute timeframe.
The difference between fixation volume and fixation duration
Being good at reading heatmaps also means that you understand the difference between the two types of data that they present. When it comes to eye tracking, fixation volume heatmaps greatly differ from fixation duration heatmaps.
Heatmaps that measure the number of eye fixations on parts of your web page are called fixation volume maps. It is when the viewer’s attention is dragged to a certain part of the page and stays there for at least 50 milliseconds.
These single spots are very important because they signify how impactful a piece of content is on your site. A red blob on the heatmap signifies that visitors have stopped their gaze at that spot multiple times. There is probably a valuable piece of content that repeatedly grabs their attention.
A fixation duration heatmap, on the other hand, measures how long visitors look at different parts of your website. It is important to distinguish between these two types of data. While fixation volume measures the frequency of looking at a certain spot, fixation duration measures the duration of it.
Remember, the first step toward measuring something is to understand what you want to measure. Using fixation volume heatmaps means that you want to know which parts of your website design attract immediate attention. These are the eye-catching parts that truly stand out.
Using fixation duration heatmaps means finding out which parts of the content your viewers are consuming the most. These sections include engaging or catchy texts and visually interesting imagery.
Understanding the pathing of each user’s eye movement is also a crucial piece of the puzzle. You can run eye-tracking studies on unfinished websites or SaaS to make improvements on them before they go live. This way, you can correct overly ambitious ideas that would have otherwise failed.
Eye tracking heatmaps pros and cons
Pros:
- With eye-tracking heatmaps, you capitalize on the fact that viewers keep their sight on things they pay attention to. This is a precise method that can record the pathing of their eye movement, revealing the elements that grab their attention on your site.
- Extremely useful for work-in-progress websites and apps that are not live yet. You can show people a range of your design ideas and layouts and watch how they respond to them. If their visual attention is in the right places, you know that you are on the right track.
Cons:
- Vendors are fully aware of the edge that eye-tracking heatmaps can give you. This is why an eye-tracking study is expensive compared to mouse-tracking solutions. Make sure to get the most out of your eye-tracking study and you are not going to need another one shortly.
- Contrary to popular belief, eye-tracking is not the best tool to use if you want to work on user experience or usability. It can certainly help, but performing simple UX research turns out to be much cheaper and better. Eye-tracking is rather designed for improving user engagement and conversion rates.
Final thoughts about heatmaps
Many successful online businesses consider heatmaps as important tools in their repertoire. If you use them the right way, they can help you stand out in the competition. By reading this article, you can consider yourself prepared to collect a huge amount of data about how visitors interact with your website.
To summarize, there are 3 things you need to keep in mind when using heatmaps:
- First off, ask yourself what exactly do you want to accomplish with heatmaps. Do you want a better design or better content placement? Do you want to improve the navigation on your website? Then, think about what type of data each heatmap represents, as we explained above. Different heatmaps can be used for different purposes.
- Do you want to implement heatmaps into your day-to-day workflow or do you rather need a one-time study? Mouse tracking codes are easy to implement, while eye-tracking studies are harder to arrange and also more expensive. Also, some heatmaps can be used on unfinished sites or software while others work better on those that are already online.
- If you came here to look for the best heatmap to use, you are starting with the wrong mindset. You will only be able to harvest the true value of heatmaps if you combine the different types.
Start using heatmaps the right way and you will end up with crucial knowledge about how users interact with your web page. While a lot can be achieved with charts and graphs, seeing your website through your viewers’ eyes is what can help you understand user behavior.



